A Comprehensive Guide to Peptides: Types, Mechanisms, Safety, and Availability
Peptides have gained immense popularity in recent years due to their wide range of benefits in health, fitness, and skincare. These short chains of amino acids serve as the building blocks of proteins and play a crucial role in various biological functions. In this blog, we will explore the different types of peptides, how they work, their safety, and where to obtain them.
Table of Contents
What Are Peptides?
Peptides are naturally occurring compounds made up of amino acids linked by peptide bonds. They act as signaling molecules within the body, regulating processes such as hormone production, immune function, and tissue repair. Depending on their structure and function, peptides can be classified into different categories, each offering unique benefits.
How Do Peptides Work?
Peptides function as biological messengers that bind to specific receptors on cells, triggering various physiological responses. Their mechanisms vary depending on the type of peptide:
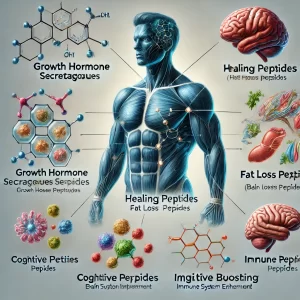
- Growth hormone secretagogues stimulate the pituitary gland to release more growth hormone, promoting muscle growth and fat loss.
- Healing peptides accelerate cell repair by enhancing blood flow and reducing inflammation.
- Nootropic peptides modulate neurotransmitters in the brain, improving cognition and mood.
- Fat loss peptides enhance lipolysis, allowing the body to break down stored fat more efficiently.
- Immune-boosting peptides enhance the function of immune cells, improving the body’s ability to fight infections.
The effectiveness of peptides depends on factors such as dosage, administration method (oral, injection, or topical), and individual physiology.
Types of Peptides and Their Benefits
1. Growth Hormone Secretagogues (GHS)
- Examples: CJC-1295, Ipamorelin, GHRP-2, GHRP-6, Hexarelin, Tesamorelin
- How They Work: These peptides stimulate the hypothalamus and pituitary gland to release growth hormone, leading to increased muscle mass, reduced fat, and faster recovery.
- Safety: Generally considered safe when used correctly, but overuse may lead to side effects such as water retention or insulin resistance.
- Where to Get: Typically available through peptide research companies and some compounding pharmacies with a prescription.
2. Healing and Recovery Peptides
- Examples: BPC-157, TB-500, KPV, Thymosin Beta-4
- How They Work: Promote tissue repair by stimulating angiogenesis (formation of new blood vessels) and reducing inflammation.
- Safety: Well-tolerated, but more long-term studies are needed to confirm their safety.
- Where to Get: Research peptide suppliers and specialty medical providers.
3. Anti-Aging and Skin Peptides
- Examples: Matrixyl, Argireline, Copper Peptides (GHK-Cu), Acetyl Hexapeptide-8, Palmitoyl Pentapeptide
- How They Work: Stimulate collagen production and reduce muscle contractions to minimize wrinkles.
- Safety: Widely used in skincare products and considered safe for topical use.
- Where to Get: Available in high-quality skincare formulations and cosmetic peptide providers.
4. Fat Loss Peptides
- Examples: AOD-9604, 5-Amino-1MQ, MOTS-c, CJC-1295 DAC
- How They Work: Enhance fat metabolism by activating lipolysis and improving mitochondrial function.
- Safety: Considered safe but may have mild side effects like nausea or headaches.
- Where to Get: Often sourced from research peptide suppliers and some wellness clinics.
5. Cognitive and Nootropic Peptides
- Examples: Selank, Semax, Cerebrolysin, Epitalon, N-Acetyl Semax Amidate
- How They Work: Modulate neurotransmitters such as dopamine and serotonin, improving cognitive function and mood.
- Safety: Generally safe but may cause mild headaches or dizziness in sensitive individuals.
- Where to Get: Available through research peptide suppliers and select pharmacies in some countries.
6. Immune System Boosting Peptides
- Examples: Thymosin Alpha-1, LL-37, Thymogen, Defensins
- How They Work: Enhance the function of immune cells like T-cells and macrophages, improving resistance to infections.
- Safety: Considered safe with minimal side effects, though high doses may lead to immune overstimulation.
- Where to Get: Available through specialized pharmacies and research suppliers.
7. Sexual Health and Libido-Boosting Peptides
- Examples: PT-141 (Bremelanotide), Kisspeptin-10, Melanotan II
- How They Work: Influence the nervous system and hormone production to increase sexual arousal and performance.
- Safety: Generally safe but may cause flushing or nausea in some users.
- Where to Get: Some forms are available via prescription, while others can be found from research suppliers.
8. Muscle Growth and Performance Peptides
- Examples: Follistatin-344, Myostatin Inhibitors, IGF-1 LR3, PEG-MGF
- How They Work: Inhibit muscle growth regulators like myostatin to enhance muscle hypertrophy.
- Safety: Potential risk of excessive muscle growth leading to imbalances; requires careful use.
- Where to Get: Usually sourced from research suppliers and specialized clinics.
9. Sleep and Recovery Peptides
- Examples: DSIP (Delta Sleep-Inducing Peptide), Epitalon
- How They Work: Regulate melatonin and other sleep-related hormones to improve deep sleep.
- Safety: Generally safe, but long-term data is limited.
- Where to Get: Available through peptide research companies.
10. Gut Health and Digestive Peptides
- Examples: BPC-157, KPV
- How They Work: Reduce inflammation in the gut lining and enhance repair of the digestive tract.
- Safety: Considered safe with minimal side effects.
- Where to Get: Found in peptide research suppliers and select medical clinics.
Are Peptides Safe?
While many peptides are considered safe, their safety depends on dosage, administration, and individual response. Some general considerations:
- Side Effects: May include water retention, headaches, nausea, or allergic reactions.
- Long-Term Data: Some peptides lack extensive long-term research.
- Regulation: Many peptides are still classified as research chemicals and are not FDA-approved for all uses.
- Quality Control: Some suppliers may provide low-quality or impure products. It is essential to source peptides from reputable companies.
Where to Get Peptides?
Peptides are available through various channels, including:
- Compounding Pharmacies: Offer high-quality, prescription-grade peptides.
- Research Peptide Suppliers: Provide peptides for laboratory and research purposes (use with caution).
- Wellness and Anti-Aging Clinics: Some offer peptide therapies under medical supervision.
- Online Retailers: Many peptides are sold online, but the quality and purity vary.
When purchasing peptides, always verify the supplier’s credentials, check for third-party testing, and consult a healthcare professional before use.
Conclusion
Peptides offer a vast range of benefits for health, longevity, and performance. Whether you seek muscle growth, cognitive enhancement, or skin rejuvenation, there is likely a peptide to meet your needs. However, their safety and effectiveness depend on proper usage, sourcing, and individual response. Always consult a healthcare professional before beginning any peptide therapy to ensure safe and effective use.